The sternal facet at the symphysis of the furcula is relatively narrower
and deeper in Morus than in Sula. The clavicular shafts are relatively
thicker in Moms than in Sula. There are usually one or more pneumatic
foraminae between the coracoidal facet and the scapular tuberosity in Morus,
but not in Sula.
On the scapula, at the anterior base of the acromion, is a pneumatic
foramen on the dorsal side in Morus and on the ventral side in Sula.
The distal end of the blade is less angular with respect to the shaft in
Morus than in Sula.
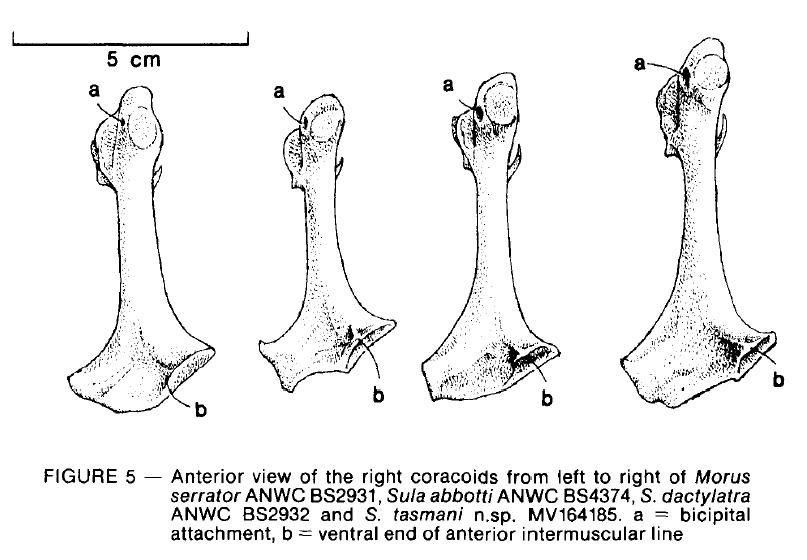
Above the anterior sternal face of the coracoid, as noted by Wetmore
(1926) and Brodkorb (1955), is a bulge in Sula and not in Morus (Figure
5). On the bulge is the anterior intermuscular line of Fisher (1945). Where
the line terminates at the sternal facet is a prominent tubercle in Sula
and not in Morus. The line ends at the sternal facet also more laterally
in Morus than in Sula. Howard (1936) reported that the anterior sternal
facet is relatively longer and narrower in Morus than in Sula, that the
dorsal end is relatively broader in Morus than in Sula, and that the bicipital
attachment is small and faintly marked in Morus but is a large and prominent
pit in Sula. From a dorsal view, the furrow between the bicipital attachment
and the glenoid facet is relatively broader in Morus than in Sula. The
sterno-coracoidal process is pointed in Morus and truncated in Sula (Figure
5).
Wing
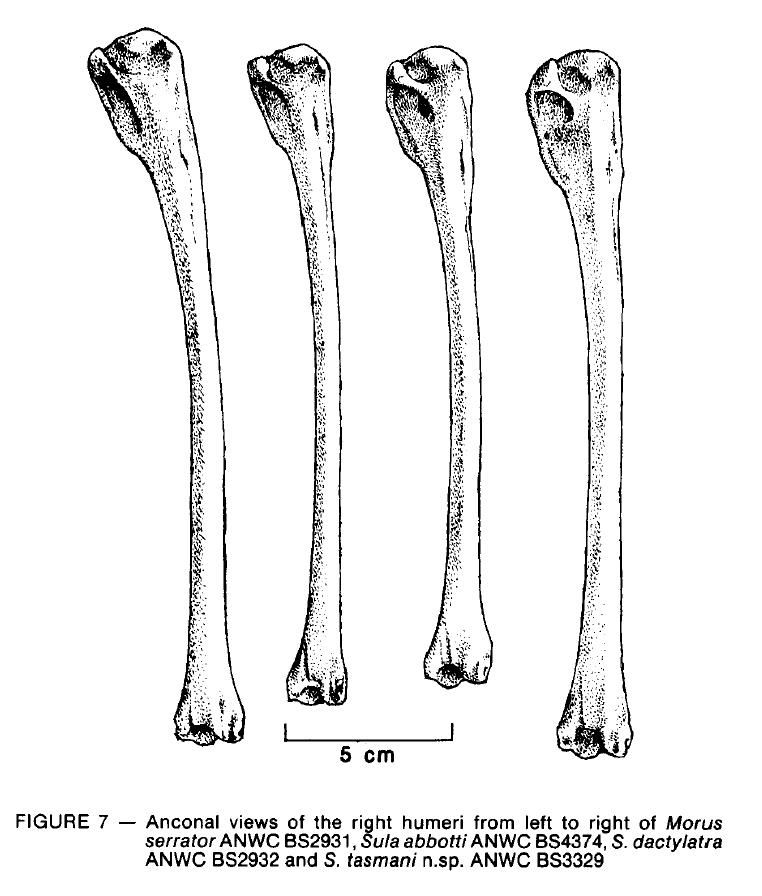
The humerus is longer than the ulna in Morus and shorter than the
ulna in Sula, including S. abbotti, where the humerus is almost as long
as the ulna (Figure 6, Shufeldt 1902, Miller 1935, Howard 1958, Bourne
1976). The median crest of the humerus extends further distally in Morus
than in Sula (Figure 7) and on the anconal or ulnar side, as indicated
by Howard (1958), the central ridge is rounded and indistinct in Morus
but is angular in Sula. At the distal end, Morus has a shallower impression
for M. brachialis anticus than Sula. On the internal side of the olecranal
fossa, Morus lacks the overhang with a few foramina under it (Wetmore
1930) that is indistinct in Sula abborri and prominent in other Sula. The
shapes of the external (= radial) condyle and the attachment for M. pronator
brevis are too variable for us to confirm any of the differences between
Morus and Sula that were suggested by Wetmore (1926, 1930, 1938).
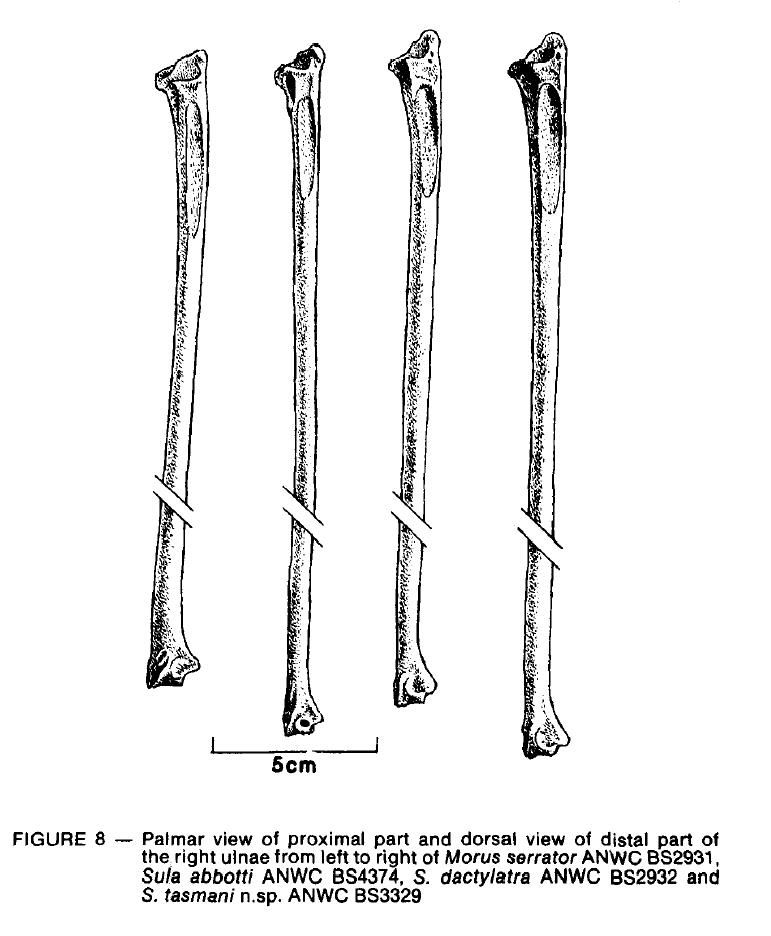
There is a foramen in the proximal radial depression of the ulna in
Sula but not in Morus (Figure 8). The impression of M. brachialis anticus
is relatively longer in Morus than in Sula. The shaft of the ulna is relatively
thicker in Moms than in Sula. Relative to the internal and external condyles
at the distal end of the ulna, the tip of the carpal tuberosity is more distal
in Sula than in Morus.
S tasmanl
t
A t A
A$ %S abbott~
S nebouxll o
A
- A A
A A S dactylatra M capens,- . ' % Mbassanus
A . 9 -
0 t . 8
0 . 1 1 1 s sula o . ;#om
l ff '0 M serrator
0 . 0
S varlegata
S leucogaster 0
oO
1 6 0 140 150 160 170 180 193 200 210 220 230 mm
At the distal end of the radius on the palmar side, relative to the
scapho-lunar facet, a prominent foramen is more proximally located in
Morus than one or more smaller foramina in Sula.
At the proximal end of the carpometacarpus, the pneumatic foramen
in the internal ligamental fossa is much larger in Morus than in Sula,
and the anterior carpal fossa has a prominent foramen in Sula and not
in Morus. In Sula a ridge extends from the external ligamental attachment
almost to the proximal end of metacarpal 111. Morus does not have this
ridge. In Sula the groove of the carpal trochlea extends farther on to
the proximal end of metacarpal I11 than in Morus. We did not find any
significant differences in the shapes of the pollical facet between Moms
and Sula, as was suggested by Brodkorb (1963b).
Pelvic girdle
On the synsacrum, the anterior articular facet of the centrum is in Morus
as deep as or deeper than it is wide, and in Sula it is as wide as or wider
than it is deep.
The caudal part of the ilium is relatively broader above and behind
the ilio-ischiatic fenestra in Sula than in Morus. The ilial process on the
caudal edge of the pelvis is small and knoblike in Moms and in Sula abbotti,
and it is large and pointed in other Sula.
Leg
The femur of Moms is longer with a relatively thinner shaft than
that of Sula. At the proximal end, the junction of the trochanter and
the trochanteric ridge is more angular in Sula than in Moms. The distal
end is relatively broader in Sula than in Moms.
The tibiotarsus of Moms is longer, with a relatively thinner shaft,
than that of Sula. The proximal and distal ends are relatively wider in
Sula than in Moms. At the proximal end, the inner cnemial crest in Moms
is hooked at the distal end and in Sula not hooked. At the distal end,
the anterior intercondylar fossa and the posterior intercondylar sulcus are
relatively wider in Sula than in Morus.